The COVID-19 pandemic also revealed the lack of secure communication channels linking authorities, institutions and citizens. Combining digital signatures and blockchain technologies in a systematic way should be able to tackle this issue. For this purpose, Danube University Krems is cooperating on the QualiSig project with A-Trust GmbH and Semotec GmbH with consulting by Jelurida Swiss SA.
The upheaval surrounding the Corona App, especially when data protection is concerned, suddenly revealed missing gaps. Still not available are secure communication channels that can also be used by citizens to exchange sensitive data that is particularly worthy of protection, for example on the state of health, between authorities and institutions commissioned by authorities or between these institutions and the public.
More security thanks to technology mix
The “QualiSig” project is aiming to resolve these problems in the field of communication by a specific combination of legally valid digital signatures (such as the relatively widespread "mobile phone signature") and modern blockchain technologies (such as the blockchains "Ardor" and "Nxt"). This combination can establish a secure connection to a person or institution. Thanks to blockchain technologies and state-of-the-art encryption methods, the storage of sensitive data is not tied to a central location and only in the hands of those involved who are to have access to it. This guarantees citizens a higher level of security in the context of COVID-19 prevention and reduces fraudulent activities.
Another project goal of "QualiSig" is to develop three near-market prototypes equipped with all necessary interfaces and the technical instructions to apply infection prevention and control. Subsequently, the authorities, bodies commissioned by authorities and NGOs can adapt and use these prototypes for appropriate purposes.
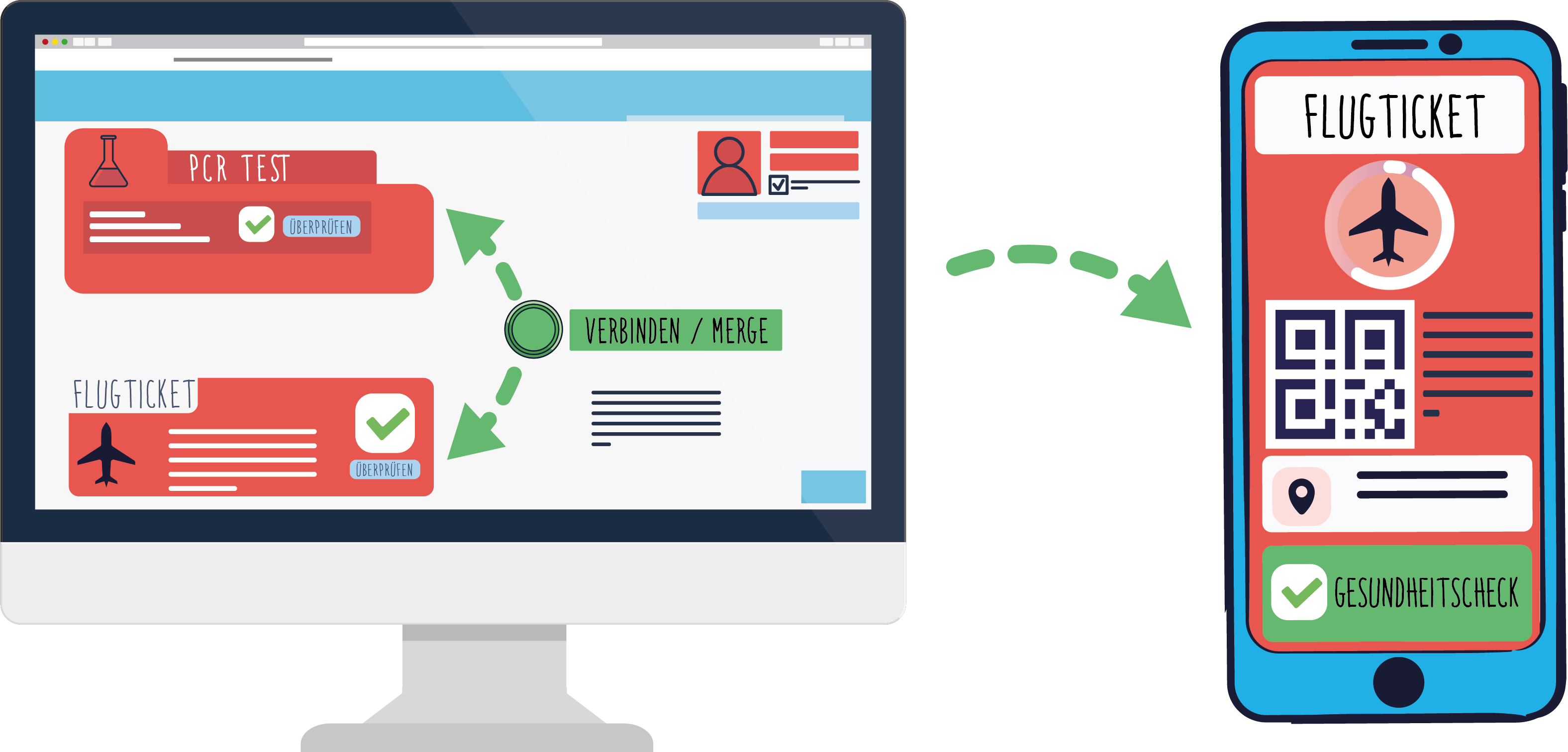
Practical applications
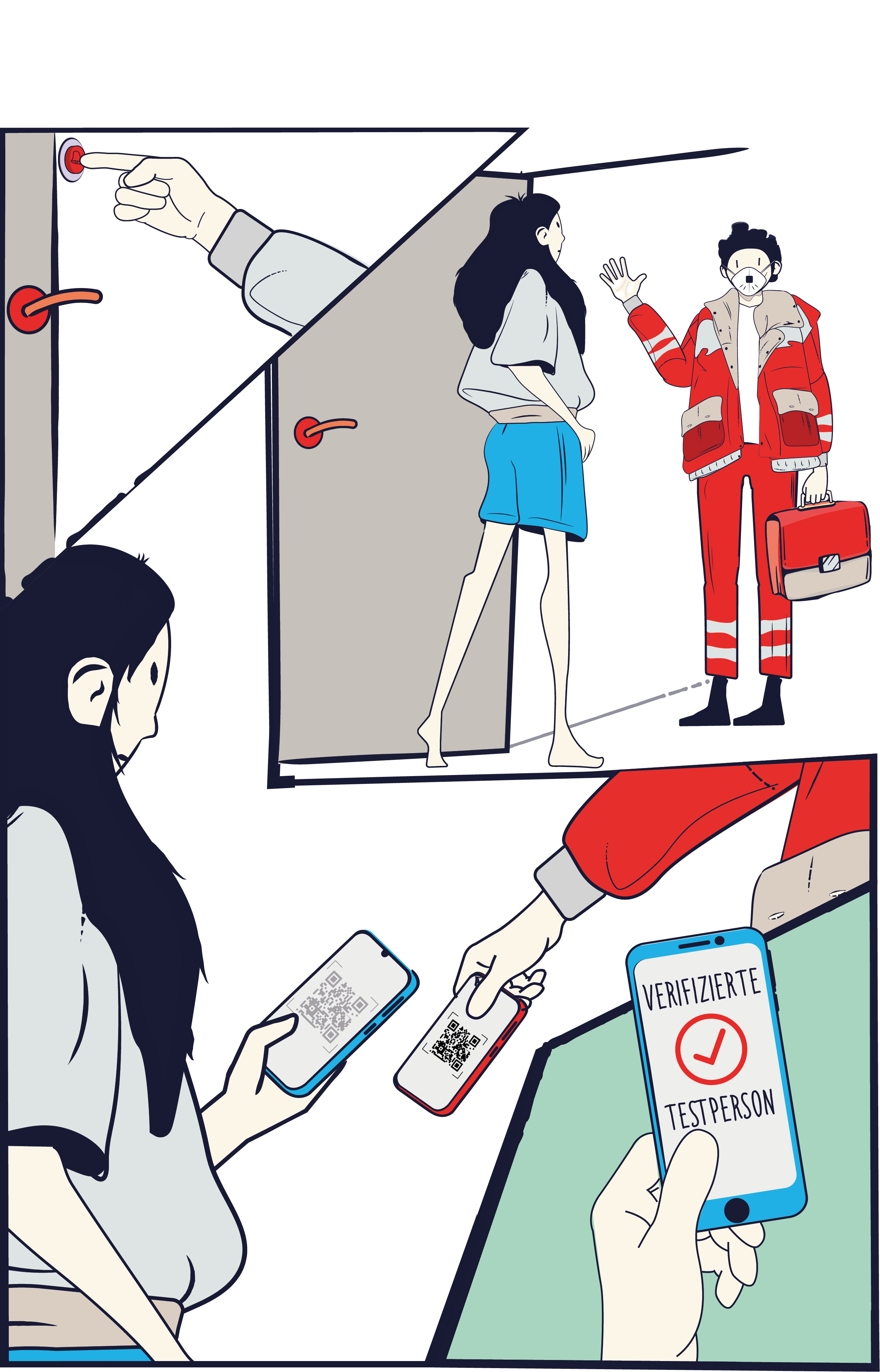
The three prototypes correspond to three typical cases of use within COVID-19 prevention. The first near-market prototype is designed for communication between citizens and the state, or bodies working on its behalf, to request COVID-19 PCR and/or antibody testing, to arrange a test appointment and to transmit the test result. Alongside other reliable information about COVID-19 such as current legal requirements or news from home and abroad could be shared. Since a digital qualified signature can verify the creator of the message, this would be an important step to prevent fake news.
The second prototype will enable citizens to use their smartphones to verify the test personnel during door-to-door tests and during (unannounced) checks of quarantine measures. Thus, the first two prototypes increase security for people.
The third prototype is dedicated to the creation of a secure digital folder for PC and smartphone to verify the health status. This will ensure the highest possible level of data protection for citizens and for all related institutions and services. At the same time, citizens should have the possibility to combine and output different data when using a smartphone. Only necessary data should be displayed on the smartphone, with the option to open the original digital documents. “The Department for E-Governance of Danube University Krems is providing advice in the area of best-practice processes in e-government and will perform an iterative test procedure for the apps created”, says the head of the department, Prof Peter Parycek.
Trust through security
The Austrian population does not like COVID-19 apps as they are perceived as unreliable. This is where the "QualiSig" project comes in and focuses on transparent and encrypted communication with the state, on tamper-proof identification of control bodies and on secure and decentralized storage of health data. Due to the decentralized and state-of-the-art encrypted storage (AES standard; from AES-128 12 words seed to AES-256 24 words seed) of sensitive ID-related data up to highly sensitive health data (proof of health or proof of immunity), the data is protected in the best possible way for all parties involved, but in particular for citizens. Any interested citizen can operate a node (data node), for example, on a smartphone or on their own PC and thus have complete control over their own data. This process asks for a special design in which no special computer knowledge is necessary. "Blockchain technologies offer enormous advantages in the area of secure data storage and allow data control by the data owner. However, a major problem is the verified origin of the data. This problem is solved by the connection between Blockchain and qualified digital identity signatures", the project initiator Alexander Pfeiffer explains the benefits of the new approach.
Project partners from the field of research and practice
Austria's leading institution in the field of qualified digital signatures (A-Trust-GmbH), secure document storage (Semotec GmbH), and Danube University Krems as a research institution are implementing the project. Danube University provides its expertise in the areas of blockchain technology through its Center for Applied Game Studies and in the area of e-government services through the Department for E-Governance and Administration.
About Emergency-Call
The COVID-19 outbreak caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 prompted the Federal Ministries for Climate Action, Environment, Energy, Mobility, Innovation and Technology and for Digital and Economic Affairs to contribute promptly 26 million euros via the FFG. In order to ensure rapid results, the emergency call will be processed in an accelerated procedure. The goal is to implement the planned projects quickly, whereby the development period may not exceed twelve months.
Tags


.jpg/jcr:content/Image%20from%20iOS%20(1).jpg)